OPSUMIT® (macitentan) was studied in SERAPHIN, the largest long-term, outcomes-based pivotal trial of an ERA in PAH1
Long-term outcomes data in both monotherapy AND combination therapy1,2
Trial design1,2:
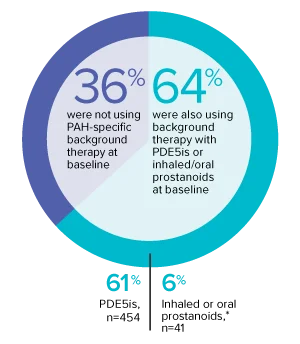
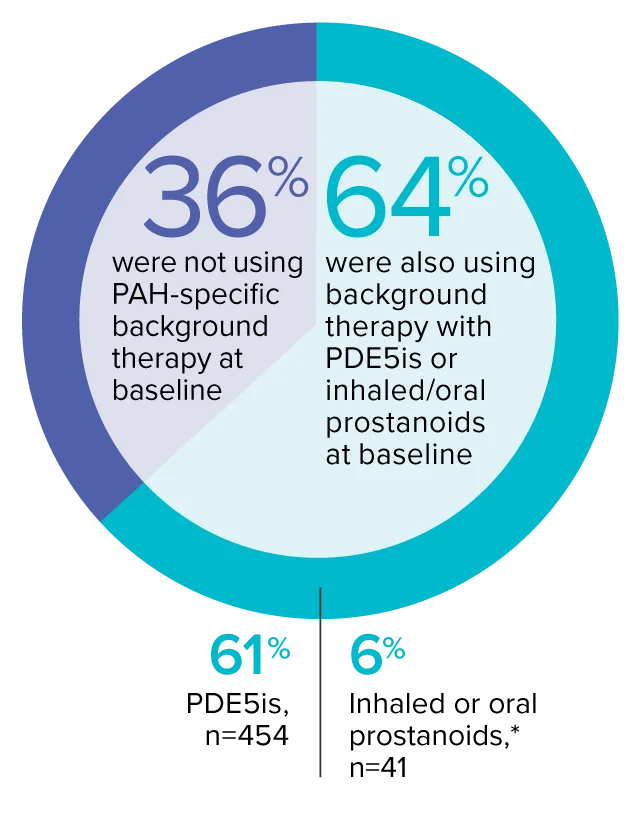
The effect of OPSUMIT® on disease progression in patients with PAH (WHO Group I) was studied in SERAPHIN, a large (N=742), event-driven, multicenter, long-term (average treatment duration 2 years), randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. At study baseline, 36% of patients were not using PAH-specific background therapy and 64% were using stable background therapy for at least 3 months with PDE5 inhibitors or inhaled/oral prostanoids.*
Trial demographics1,3:
- Patients had predominantly WHO FC II (52%) and FC III (46%) symptoms
- Etiologies included IPAH/HPAH (57%), PAH-CTD (31%), PAH-CHD with repaired shunts (8%), PAH associated with drugs and toxins (3%), and PAH-HIV (1%)
- Mean patient age was 46 years, and 77% of patients were female
- 25% of patients were recently diagnosed (<6 months) and 75% were previously diagnosed (≥6 months)
Trial demographics1
742
Patients were randomized
Macitentan 3 mg is not
an approved dose.
Monotherapy and
combination therapy1,3
*Patients were treated with OPSUMIT® monotherapy or in combination with phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors or inhaled prostanoids.1
REPAIR study
EXPLORE ANALYSIS7-Year Data
EXPLORE ANALYSISSERAPHIN: Primary endpoint in overall study population†
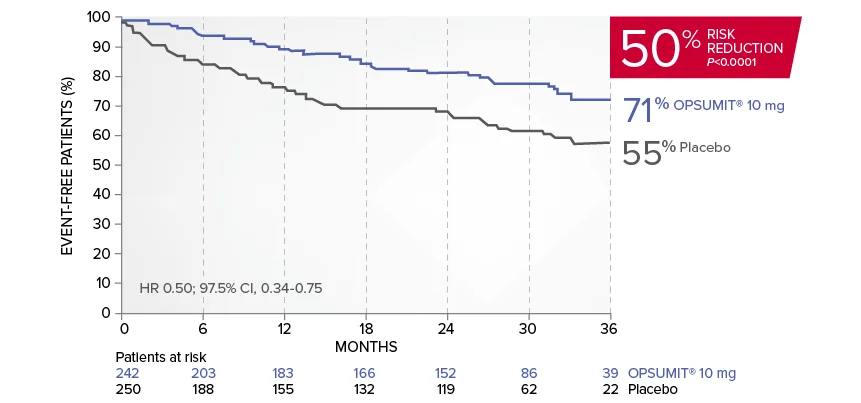
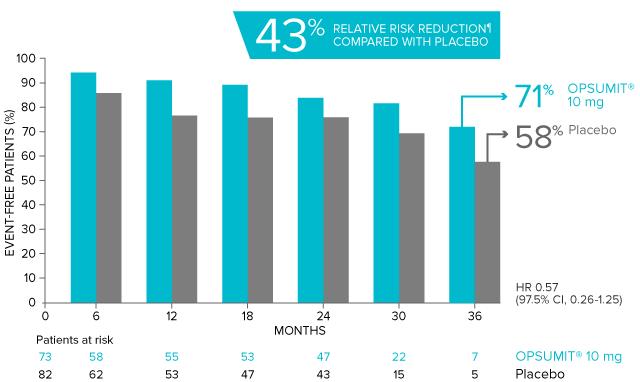
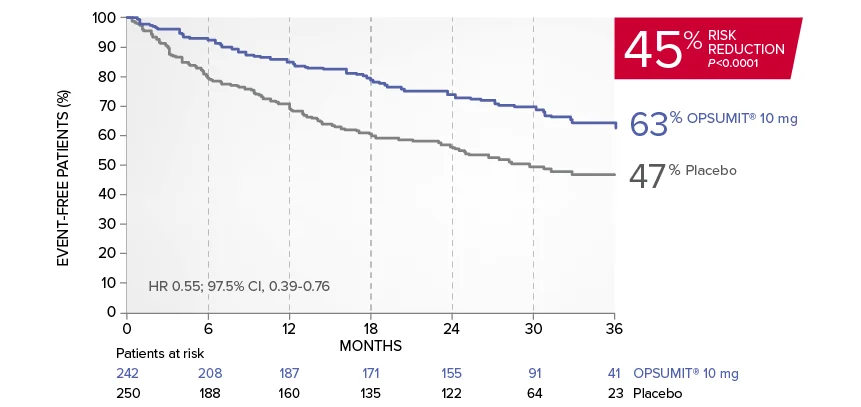
OPSUMIT® (macitentan) significantly reduced the risk of disease progression by 45% vs placebo1
The primary endpoint in the SERAPHIN trial was time to the first occurrence of death, a significant morbidity event, defined as atrial septostomy, lung transplantation, initiation of IV or SC prostanoids, or clinical worsening of PAH (defined as all of the following: a sustained ≥15% decrease from baseline in 6MWD,‡ worsening of PAH symptoms,§ and need for additional PAH treatment) during double-blind treatment plus 7 days.1,2
Kaplan-Meier estimates of risk of first primary endpoint event in SERAPHIN1,2
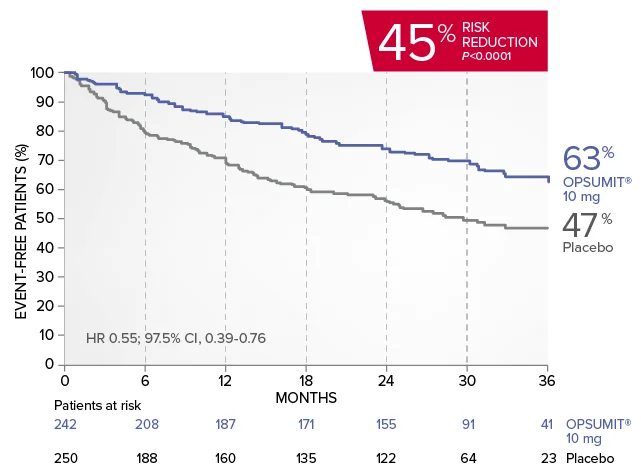
Summary of primary endpoint events1
| OPSUMIT® 10 mg (n=242), n (%) |
Placebo (n=250), n (%) |
|
|---|---|---|
| Patients with a primary endpoint event‖ | 76 (31.4) | 116 (46.4) |
| Component as first event | ||
| Worsening PAH | 59 (24.4) | 93 (37.2) |
| Death | 16 (6.6) | 17 (6.8) |
| Initiation of IV/SC prostanoids | 1 (0.4) | 6 (2.4) |
The beneficial effect of OPSUMIT® was primarily attributable to a reduction in clinical worsening events (defined as all of the following: a sustained ≥15% decrease from baseline in 6MWD,† worsening of PAH symptoms [a decline in WHO FC], and need for additional PAH treatment).
‖No patients experienced an event of lung transplantation or atrial septostomy in the placebo or OPSUMIT® 10 mg treatment groups.
OPSUMIT® can be started as monotherapy or in combination with PDE5 inhibitors or inhaled prostanoids.1*
*Patients were treated with OPSUMIT® monotherapy or in combination with phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors or inhaled prostanoids.1
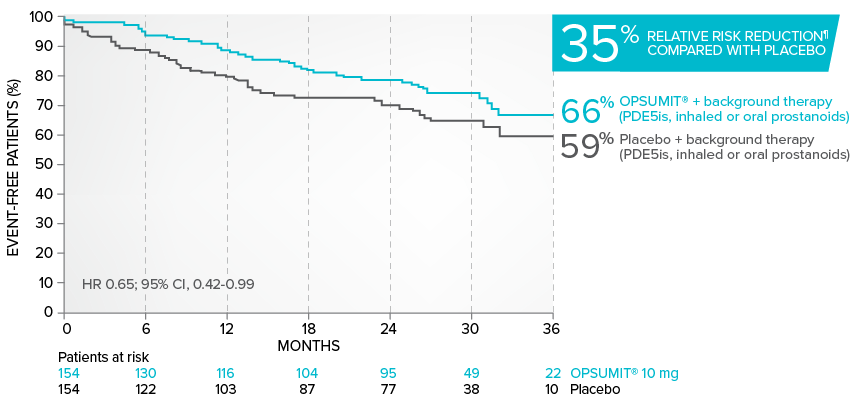
Combination therapy exploratory subgroup analysis in SERAPHIN trial
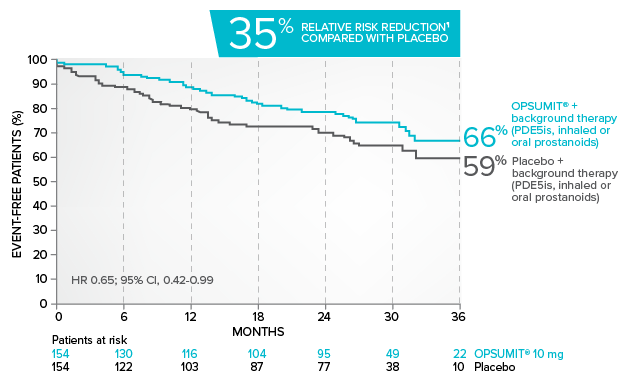
Kaplan-Meier estimates of risk of primary endpoint event when OPSUMIT® was added to stable PAH-specific background therapy1,3
At baseline, 64% of enrolled patients were treated with a stable dose of PAH-specific background therapy (61% PDE5 inhibitors; 6% inhaled or oral prostanoids).1*
*Patients were treated with OPSUMIT® monotherapy or in combination with phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors or inhaled prostanoids.1
Kaplan-Meier estimates of risk of first primary endpoint event1,3,4
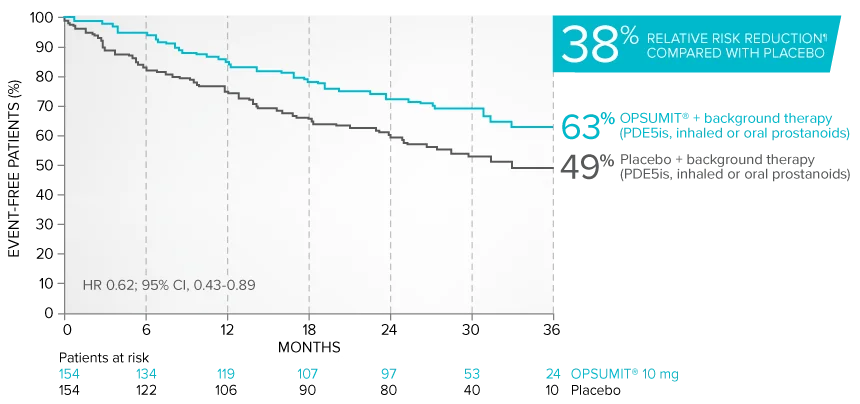
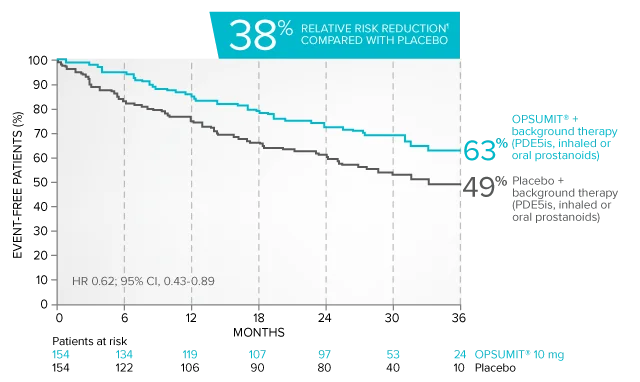
¶Not adjusted for multiplicity.
Summary of primary endpoint events in patients treated with PAH-specific background therapy4
| OPSUMIT® 10 mg (n=154), n (%) |
Placebo (n=154), n (%) |
|
|---|---|---|
| Patients with a primary endpoint event‖ | 50 (32.5) | 68 (44.2) |
| Component as first event | ||
| Worsening PAH | 39 (25.3) | 58 (37.7) |
| Death | 10 (6.5) | 6 (3.9) |
| Initiation of IV/SC prostanoids | 1 (0.6) | 4 (2.6) |
‖No patients experienced an event of lung transplantation or atrial septostomy in the placebo or OPSUMIT® 10 mg treatment groups.
Common adverse reactions in the combination therapy exploratory subgroup5#
| OPSUMIT® 10 mg n=154 |
Placebo n=153 |
|
|---|---|---|
| Anemia | 16.2% | 4.6% |
| Nasopharyngitis | 11.0% | 10.5% |
| Bronchitis | 11.0% | 5.9% |
| Headache | 13.6% | 10.5% |
| Diarrhea | 13.0% | 9.8% |
#More frequent than placebo by ≥3%.
Combination therapy exploratory subgroup safety2,5
- The safety profile of OPSUMIT® as part of a combination therapy regimen was consistent with that of OPSUMIT® in the overall SERAPHIN population
- The incidence of peripheral edema, a known ERA-related adverse event, was similar in OPSUMIT®- and placebo-treated patients receiving background therapy (19.5% and 23.5%, respectively)
- Treatment discontinuations due to adverse events in patients receiving background therapy were similar in those receiving OPSUMIT® and those receiving placebo (9.1% and 11.8%, respectively)
Looking for patient enrollment resources?
Enroll PatientsSERAPHIN PAH-related hospitalization results
View the DataPAH-related hospitalization
OPSUMIT® (macitentan) reduced the risk of PAH-related hospitalization1,2
A key secondary endpoint in SERAPHIN was death due to PAH or PAH-related hospitalization.
There was a 50% reduction in the risk of PAH-related hospitalization vs placebo in the overall population.†
Kaplan-Meier estimates of risk of first key secondary endpoint event1,2
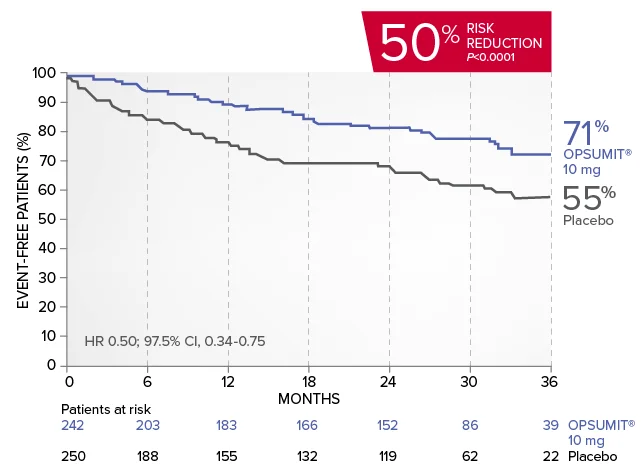
Summary of death due to PAH and hospitalization due to PAH1,2
| OPSUMIT® 10 mg (n=242), n (%) |
Placebo (n=250), n (%) |
|
|---|---|---|
| Death due to PAH or hospitalization for PAH | 50 (20.7) | 84 (33.6) |
| Component as first event | ||
| Death due to PAH | 5 (2.1) | 5 (2.0) |
| Hospitalization for PAH | 45 (18.6) | 79 (31.6) |
Exploratory subgroup analysis: Combination therapy results
Kaplan-Meier estimates of risk of first key secondary endpoint event when OPSUMIT® was added to stable PAH-specific background therapy6
- At baseline, 64% of enrolled patients were treated with a stable dose of PAH-specific background therapy (61% PDE5 inhibitors; 6% inhaled or oral prostanoids). Patients were treated with OPSUMIT® monotherapy or in combination with phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors or inhaled prostanoids.1
Kaplan-Meier estimates of risk of first key secondary endpoint event6
Summary of death due to PAH and hospitalization due to PAH6
| OPSUMIT® 10 mg (n=154), n (%) |
Placebo (n=154), n (%) |
|
|---|---|---|
| Death due to PAH or hospitalization for PAH | 37 (24.0) | 49 (31.8) |
| Component as first event | ||
| Death due to PAH | 2 (1.3) | 2 (1.3) |
| Hospitalization for PAH | 35 (22.7) | 47 (30.5) |
Common adverse reactions in the combination therapy exploratory subgroup5#
| OPSUMIT® 10 mg n=154 |
Placebo n=153 |
|
|---|---|---|
| Anemia | 16.2% | 4.6% |
| Nasopharyngitis | 11.0% | 10.5% |
| Bronchitis | 11.0% | 5.9% |
| Headache | 13.6% | 10.5% |
| Diarrhea | 13.0% | 9.8% |
#More frequent than placebo by ≥3%.
Combination therapy exploratory subgroup safety2,5,6
- The safety profile of OPSUMIT® as part of a combination therapy regimen was consistent with that of OPSUMIT® in the overall SERAPHIN population
- The incidence of peripheral edema, a known ERA-related adverse event, was similar in OPSUMIT®- and placebo-treated patients receiving background therapy (19.5% and 23.5%, respectively)
- Treatment discontinuations due to adverse events in patients receiving background therapy were similar in those receiving OPSUMIT® and those receiving placebo (9.1% and 11.8%, respectively)
†All randomized patients.
¶Not adjusted for multiplicity.
Looking for patient enrollment resources?
Enroll PatientsOPSUMIT® (macitentan): Additional endpoints from the SERAPHIN trial
SERAPHIN included secondary and exploratory endpoints from baseline to Month 6
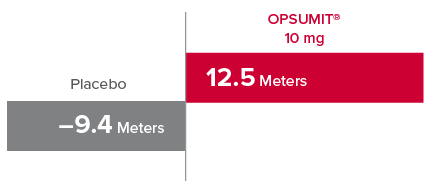
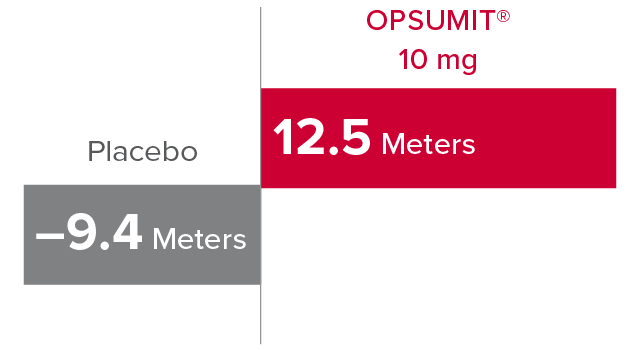
Change from baseline in 6MWD at Month 61,2
At Month 6, 6MWD had increased by a mean of 12.5 m in the group receiving OPSUMIT® 10 mg (n=242); 6MWD decreased by a mean of 9.4 m in the placebo group (n=249) (placebo-corrected mean increase of 22.0 m; 97.5% CI, 3.0-41.0; P=0.0078).
Change in 6MWD at Month 6
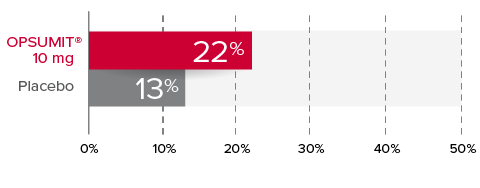
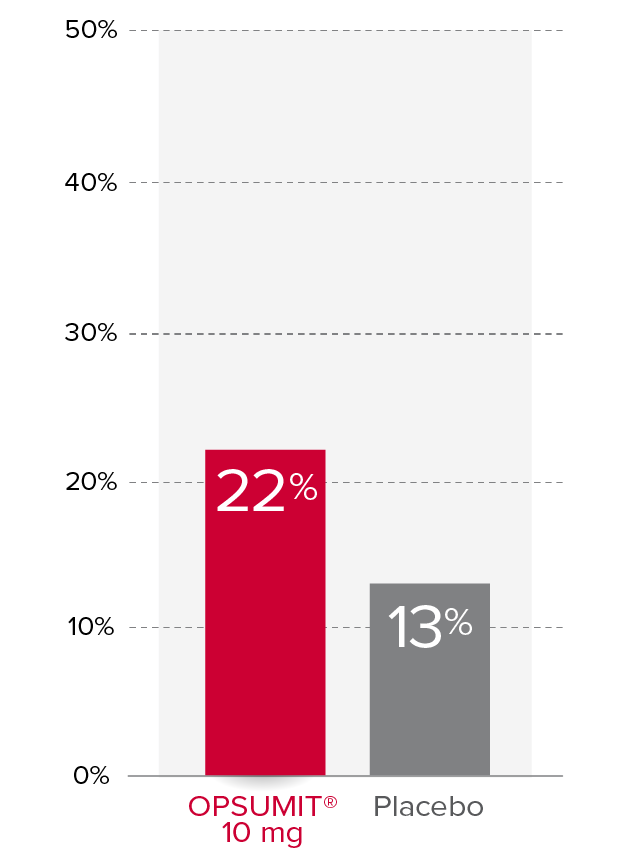
Changes from baseline in WHO FC1,2
At Month 6, 22% of patients in the OPSUMIT® 10 mg group (n=242) experienced improvement of at least 1 WHO FC vs 13% of patients in the placebo group (n=249) P=0.006.
% Patients with improvement of at least
1 WHO
FC at
Month 6
Change from baseline in measures of hemodynamics at Month 61,7,8
Exploratory hemodynamic substudy within SERAPHIN (OPSUMIT®: n=57, placebo: n=67).
PVR¶
37%
median reduction
in PVR vs
placebo
(95% CI, 22-49)
Mean PVR at BL
for OPSUMIT®:
924 ± 532
dyn•sec/cm**
Cardiac Index¶
0.6
L/min/m2
median increase
in cardiac index vs placebo
(95% CI, 0.3-0.9)
Mean cardiac index
at BL for OPSUMIT®:
2.55 ± 0.85
L/min/m2**
¶Not adjusted for multiplicity.
**Plus-minus values are mean ± standard deviation.
SERAPHIN PAH-related hospitalization results
View the DataView SERAPHIN PAH-CTD subgroup data
See the DataPAH associated with connective tissue disease (PAH-CTD)
PAH: A potential complication of CTD affecting up to approximately 1 in 10 patients9
PAH is a well-known complication in some patients with CTD10:
- PAH affects approximately 3% to 13% of patients with CTD and 5% to 12% of patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc)9,11
- Patients with PAH-SSc have a worse prognosis than most other PAH-associated disease populations12
Exploratory subgroup analysis: Disease progression in patients with PAH-CTD
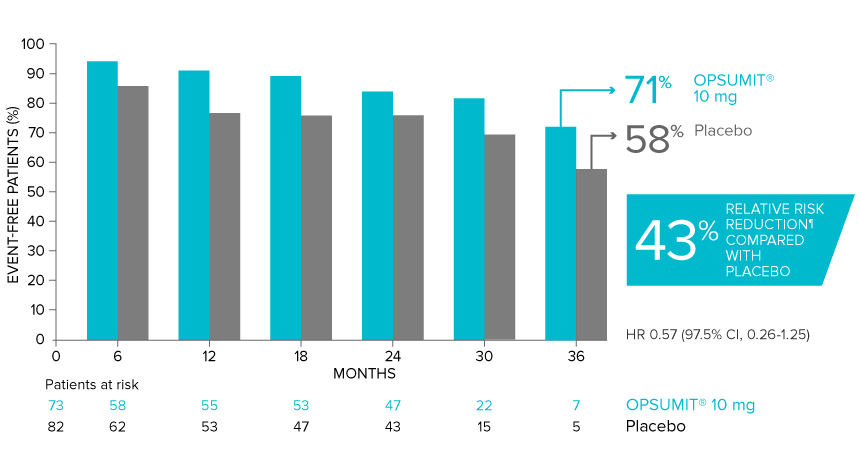
Overall, in SERAPHIN, OPSUMIT® (macitentan) reduced the risk of disease progression by 45% vs placebo (HR 0.55; 97.5% CI, 0.39-0.76; P<0.0001).1 In the SERAPHIN trial, 31% of the overall patient population had PAH-CTD.1
POST HOC ANALYSIS: Time to first disease progression event in patients with PAH-CTD13,14
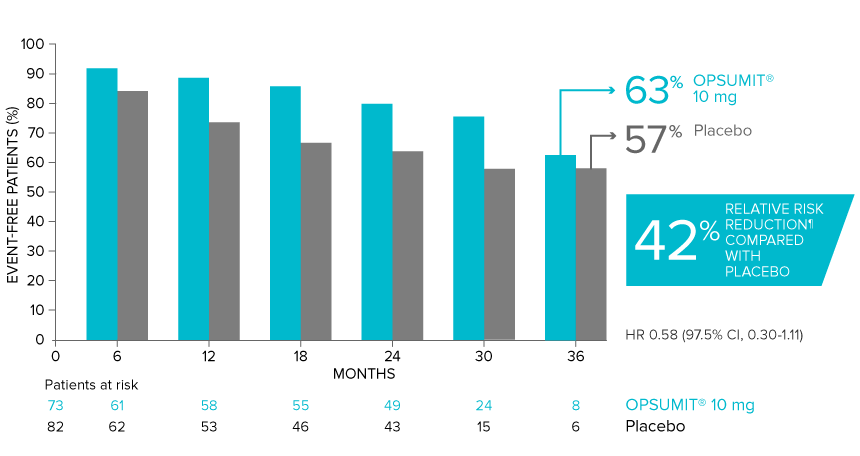
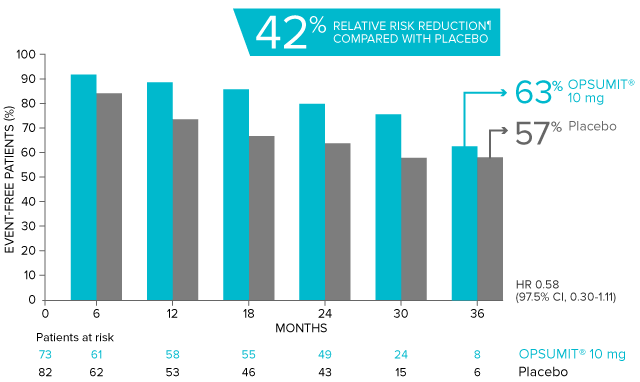
Summary of primary endpoint events in patients with PAH-CTD13
| OPSUMIT® 10 mg (n=73), n (%) |
Placebo (n=82), n (%) |
|
|---|---|---|
| Patients with a primary endpoint event* | 20 (27.4) | 31 (37.8) |
| Component as first event | ||
| Worsening PAH | 16 (21.9) | 25 (30.5) |
| Death | 3 (4.1) | 5 (6.1) |
| Initiation of IV/SC prostanoids | 1 (1.4) | 1 (1.2) |
*No patients experienced an event of lung transplantation or atrial septostomy in the placebo or OPSUMIT® 10 mg treatment groups.
Differences in PAH-CTD subgroup baseline characteristics compared with SERAPHIN overall population2,13
- Larger percentage of female patients (92% vs 76.5%)
- Older average age (49.7 years vs 45.6 years)
- Larger percentage of patients with WHO FC II symptoms (58.5% vs 52.4%)
- Lower percentage of patients with WHO FC Ill symptoms (39.3% vs 45.6%)
- Shorter time from diagnosis (mean 2.0 years vs 2.7 years)
Adverse reactions in the PAH-CTD subgroup different from the overall population13††
| OPSUMIT® 10 mg n=73 |
Placebo n=82 |
|
|---|---|---|
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 23.3% | 13.4% |
| Urinary tract infection | 12.3% | 6.1% |
| Skin ulcer | 9.6% | 3.7% |
| Sinusitis | 6.8% | 1.2% |
| Lower respiratory tract infection | 5.5% | 1.2% |
| Nausea | 8.2% | 4.9% |
††Only adverse reactions occurring ≥3% on OPSUMIT® compared with placebo and placebo-corrected difference of ≥3% in the PAH-CTD subgroup vs the overall population are shown here.
Eight (9.8%) patients receiving placebo and 8 (11.0%) patients receiving OPSUMIT® 10 mg in the PAH-CTD subgroup discontinued treatment due to adverse reactions, compared with approximately 11% for both the placebo and OPSUMIT® in the overall population.2,13
Exploratory subgroup analysis: PAH-related hospitalization
Overall, in SERAPHIN, OPSUMIT® reduced the risk of PAH-related hospitalization by 50% vs placebo (HR 0.50; 97.5% CI, 0.34-0.75; P<0.0001).1
POST HOC ANALYSIS: Time to PAH-related
death or
hospitalization in patients with PAH-CTD13,15
PAH-CTD Subgroup: Summary of death due to PAH and hospitalization due to PAH13
| OPSUMIT® 10 mg (n=73), n (%) |
Placebo (n=82), n (%) |
|
|---|---|---|
| Death due to PAH or hospitalization for PAH | 13 (17.8) | 22 (26.8) |
| Component as first event | ||
| Death due to PAH | 1 (1.4) | 1 (1.2) |
| Hospitalization for PAH | 12 (16.4) | 21 (25.6) |
Looking for patient enrollment resources?
Enroll PatientsSERAPHIN PAH-related hospitalization results
View the Data‡Confirmed by a 6-minute walk test performed on a different day within 2 weeks.
§Worsening of PAH included at least one of the following: Advancing to a higher FC from baseline (or no change in WHO FC IV) and signs of right heart failure that does not respond to oral diuretic treatment.
¶Not adjusted for multiplicity.
#More frequent than placebo by ≥3%.
**Plus-minus values are mean ± standard deviation.
6MWD=6-minute walk distance; BL=baseline; CI=confidence interval; CTD=connective tissue disease; ERA=endothelin receptor antagonist; FC=Functional Class; HPAH=heritable PAH; HR=hazard ratio; IPAH=idiopathic PAH; IV=intravenous; PAH=pulmonary arterial hypertension; PAH-CHD=PAH associated with congenital heart disease; PAH-CTD=PAH associated with connective tissue disease; PAH-HIV=PAH associated with human immunodeficiency virus; PAH-SSc=PAH associated with systemic sclerosis; PDE5i=phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor; PVR=pulmonary vascular resistance; SC=subcutaneous; SERAPHIN=Study with an Endothelin Receptor Antagonist in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension to Improve CliNical Outcome; WHO=World Health Organization.